Music Audio and Motion Capture (MAMC) Project:
Music performance AI with cross-modal and cross-cultural data
音樂聲音與3D動作追蹤(MAMC)研究計畫:
跨模組與跨文化的音樂演奏AI模型

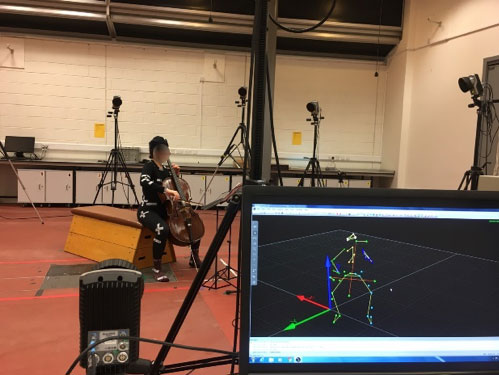

This project systematically collected and recorded a professional-level, large-scale MAMC dataset covering diverse types music performance (6420 recordings by 64 professional musicians, > 1,000,000 musical notes, > 230,000 seconds recorded). High-quality cross-modal data including 3D motion capturing of musicians’ 32 body joints, high-resolution audio recordings, and musicians’ note-by-note professional annotations regarding high-level aesthetic semantics are collected. Innovative technologies including 3D motion capture system, Music Information Retrieval (MIR) techniques, and deep learning models such as Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Sequence generative adversarial networks (SeqGAN) are applied to analyzing musicians’ performed audio and body movement.
音樂聲音與3D動作追蹤(Music Audio and Motion Capture, MAMC)是由中央研究院提供研究經費的兩年期研究計畫,旨在:1) 建置音樂演奏的大型研究資料庫,包括高準確度的音樂演奏身體動作追蹤資料(3-D motion capture)、高品質演奏錄音,以及專業音樂家對於演奏錄音的語意標註(semantic annotation); 2) 發展能夠連結局部(micro-level)聲音/動作訊號特徵及整體(macro-level)音樂語意(semantics)的跨模組(cross-modal)及跨文化(cross-cultural)模型。音樂聲音與動作追蹤計畫是隸屬於自動音樂動畫生成(Automatic Music Concert Animation, AMCA)計畫中的子計畫,AMCA是由中央研究院資訊科學研究所資助的核心計畫,旨在使用人工智慧生成多媒體內容。
本研究中大規模及系統化的跨模組音樂演奏資料收集和分析,為音樂演奏大數據中不同演奏版本間的相互比較提供了重要的基礎,本研究與跨國的研究團隊合作,包括來自英國愛丁堡大學音樂系、英國愛丁堡大學運動科學系、國立陽明交通大學物理治療系、台北藝術大學傳統音樂系,以及中央研究院資訊科學研究所的學者。
Guqin performance analysis using Music Information Retrieval (MIR) techniques
使用音訊處理技術分析古琴演奏技巧
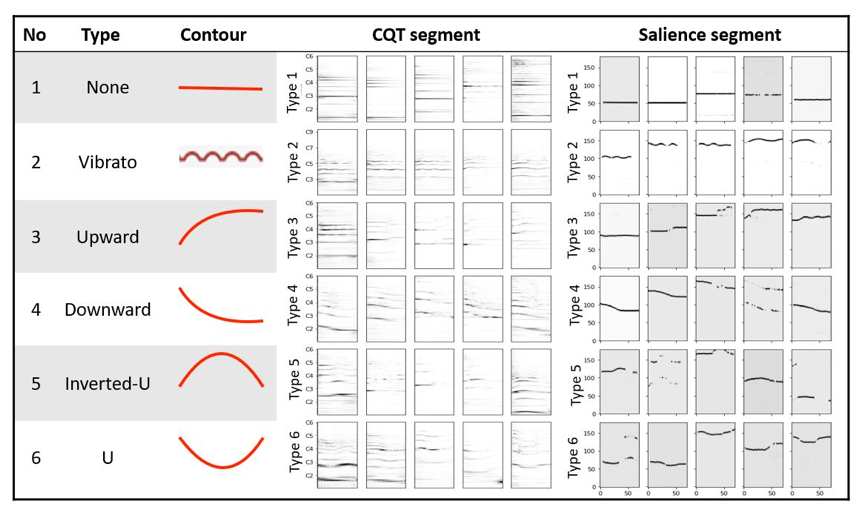

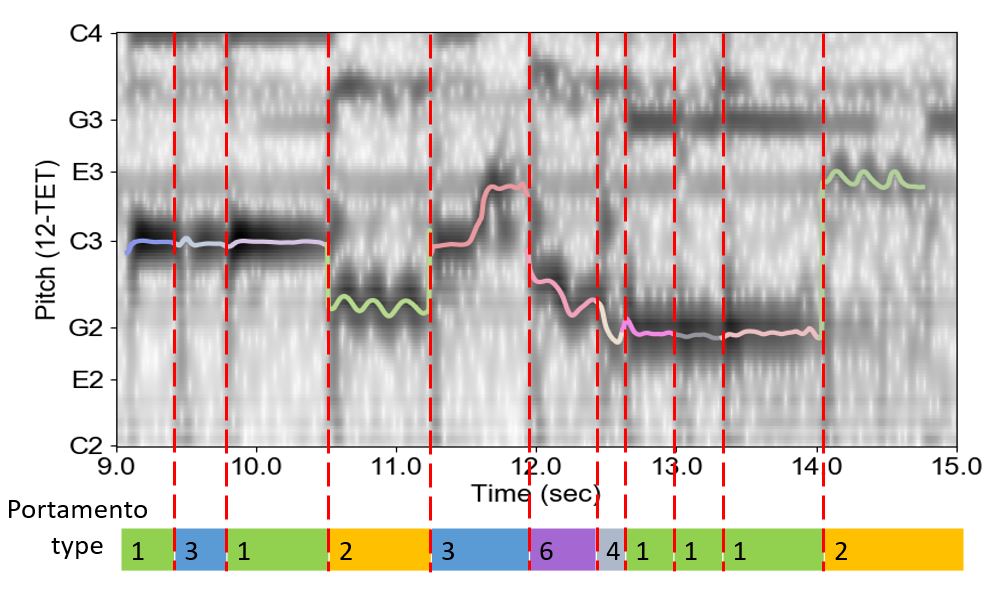
The research applies Music Information Retrieval and deep learning techniques to analyze Guqin music, and aims to explore the connection between the global tonal structure in the music piece and the implemented playing techniques in Guqin performance. Incorporating mode and playing technique analysis, this study demonstrates that the structural relationship between notes is crucial for detecting mode, and such information also provides extra guidance for the playing technique detection in local-level. In this study, a new dataset is compiled for Guqin performance analysis. The mode detection is achieved by pattern matching, and the predicted results are conjoined with audio features to be inputted into the Convolutional Neural Network for playing technique detection. It is manifest in the results that the global and local features are inter-connected in Guqin music. Our analysis identifies key components affecting the recognition of mode and playing technique, and challenging cases resulting from unique properties of Guqin audio signal are discussed for further research.
本研究使用音樂資訊檢索技術(Music Information Retrieval, MIR)及AI模型分析中國五聲音階的調式結構與古琴左手演奏手法的關聯性,古琴的歷史演奏錄音經過專家的收集及標註,本研究發展了模式比對(pattern match)的演算法,根據樂曲的錄音檔案進行自動的樂曲調式結構分析,而左手演奏手法則使用AI模型中的卷積神經網絡(Convolutional Neural Network)進行自動分類,分析結果顯示左手演奏手法的分佈情況符應了樂曲的整體調式結構,在研究中也討論了古琴與其它撥弦樂器不同的獨特聲音特質。
Expressive semantics in orchestral conducting movement
樂團指揮動作的音樂表現語彙
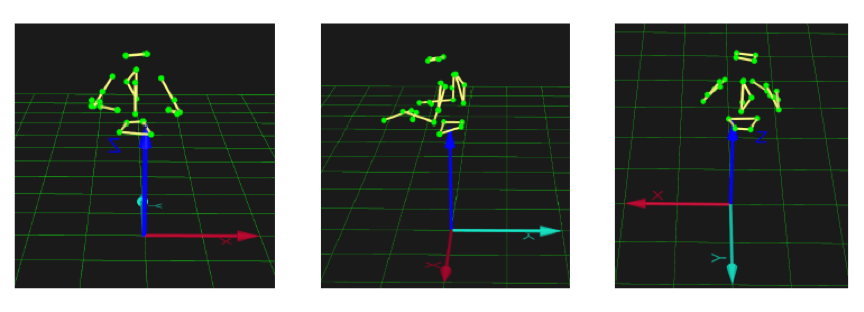
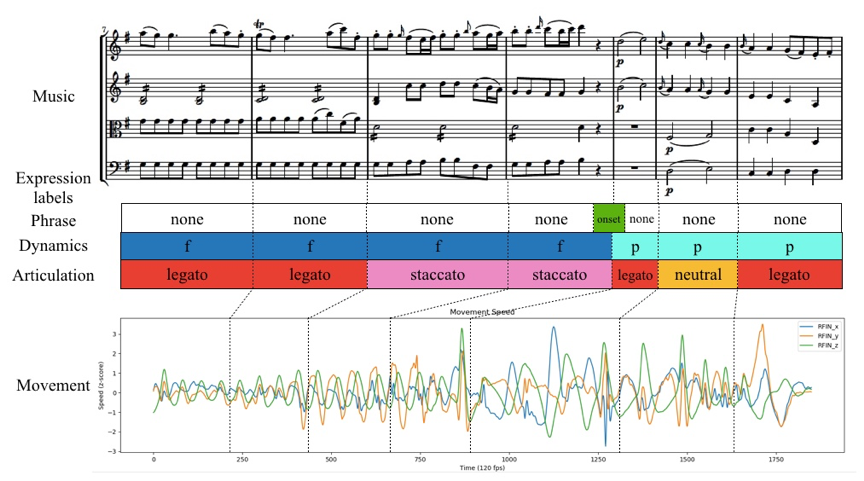
In this research, we seek to explore an approach to search for effective descriptors in conducting movement to express musical features, and to extract complex expressive semantics from elementary conducting kinematic variations in a valid musical context. This study proposes a multi-task learning model to jointly identify dynamic, articulation, and phrasing cues from conducting kinematics. A professional conducting movement dataset is compiled using a high-resolution motion capture system. ReliefF algorithm is applied to select significant features from conducting movement, and recurrent neural network (RNN) is implemented to identify multiple movement cues. The experimental results disclose the key elements in conducting movement to communicate musical expressiveness, as well as to highlight the advantage of multi-task learning in the complete musical context over single-task learning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to explore multiple semantic expressive cuing in conducting movement kinematics using recurrent neural network.
本研究探索樂團指揮家的動作語彙(movement semantics),3-D動作追蹤(motion capture)技術被應用於錄製樂團指揮家的身體動作,並分析指揮動作的運動力學(kinematic)特徵,特徵選擇(feature selection)的演算法辨認出動作中的主要特徵,此些特徵並經由AI模型中的遞歸神經網路(Recurrent Neural Network)自動分類,辨識出指揮動作中關於樂句、力度,以及演奏技巧(articulation) 的指示。
